Top B2B SaaS Subscription Pricing Models and Their Pros and Cons
Subscription pricing is the go-to standard in the B2B SaaS industry. It helps brands generate recurring revenue while offering clients greater flexibility by breaking down the cost of premium software into smaller, manageable payments.
While the benefits of subscription billing are clear, it can be difficult to choose the right model for your business. Not only do you have to ensure your price points match the value of your software, but they should also correlate with the needs of your customers.
To help you make the right choice, this article discusses the popular B2B SaaS subscription pricing models alongside their pros and cons.
1. Freemium
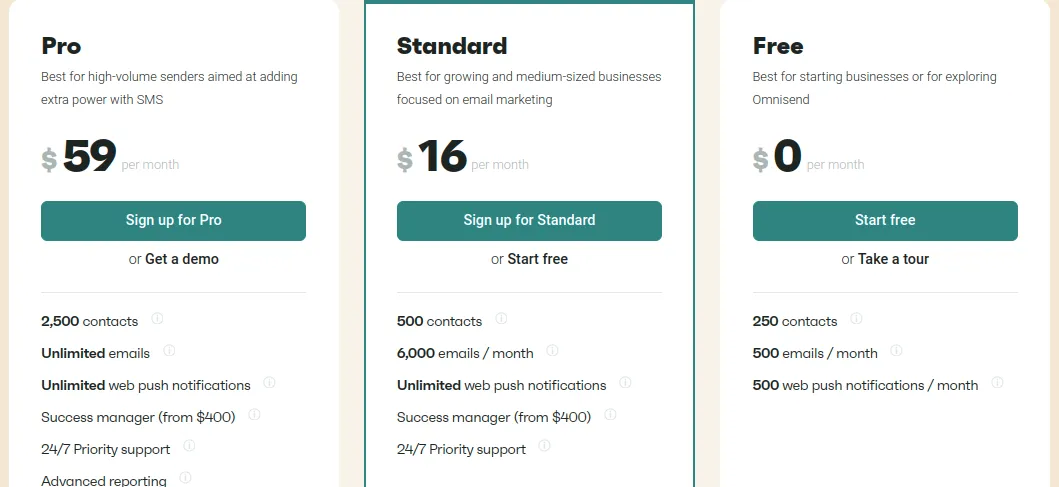
In a freemium pricing model, clients have limited access to a software for free but have to subscribe to a paid plan to access premium features. Generally, the free plan is designed to hook clients and get them to experience your product. If they want more, they’ll have to upgrade to a premium subscription or pay for add-on services.
Should you choose this model, you need to decide which features to offer for free and the ones clients need to pay for to access. Finding the right balance can be difficult because your free offering should be compelling enough without giving too much away. Otherwise, customers will not see the need to upgrade to a paid plan, thus limiting your revenue potential.
A good example of a brand with a freemium model is Omnisend. The email marketing services company has a robust free plan with pre-set usage limits. As client needs grow beyond the usage limits of the free plan, they’re compelled to upgrade to a premium plan to unlock more features.

Pros
- Low barrier to entry
- Free plan allows brands to prove the product’s value to customers
- Provides lots of useful customer information for upselling
Cons
- It’s easy to give too much away in the free plan
- Requires significant effort to upsell users to a premium plan
2. Tiered Pricing
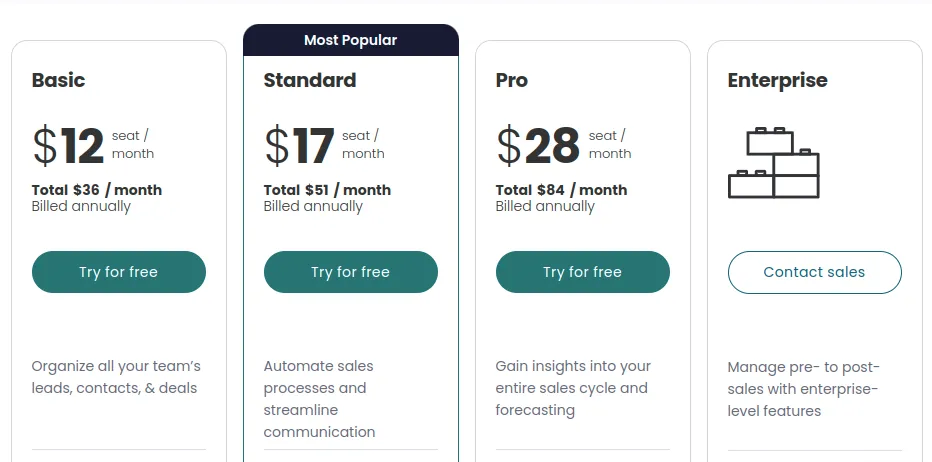
The tiered pricing model is one of the most popular subscription models for B2B SaaS businesses. According to the Attrock guide, businesses with different product packages use a subscription management solution to cater to the diverse needs of their clients.
The tiers are usually built around features and volume, with the higher-tiered plans offering advanced features and usage access.
When optimized correctly, a tiered subscription model gives your clients greater flexibility as they can choose a plan that works for them at any given time. It also provides a structured path for upselling as you can easily market the advanced features clients need as their operations grow.
Monday.com is a great example of a B2B SaaS with tiered pricing.
Pros
- Caters to different audiences, from beginners to advanced users
- Provides a structured upsell path
- Allows you to create tiers based on features, resources, or volume
Cons
- Can be difficult to design tiers and set the right price points
- Account management can be complicated
3. Usage-based Pricing
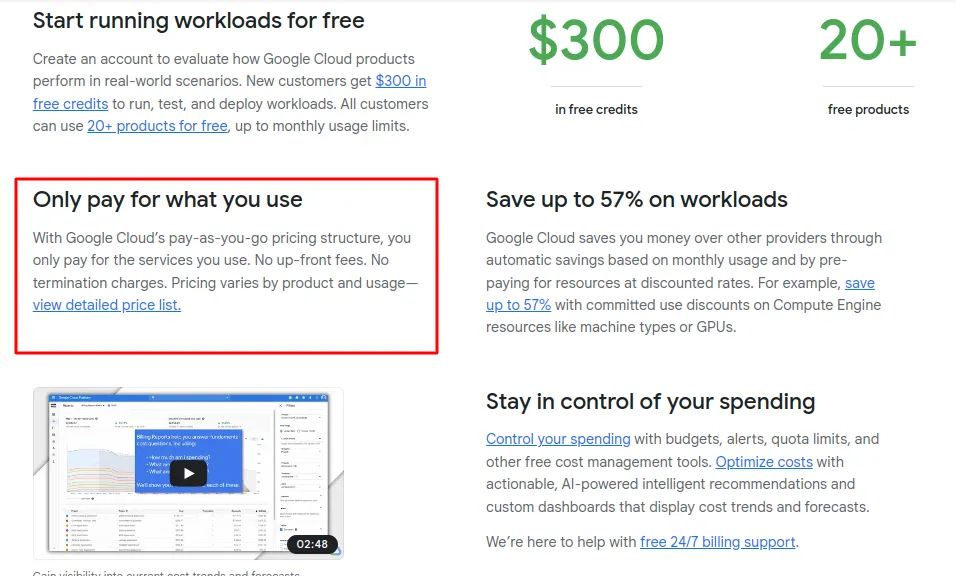
Also known as pay-as-you-go (PAYG), usage-based pricing is a subscription model where customers pay according to their consumption levels. The more they use, the more they pay, and vice versa.
According to Younium SaaS revenue recognition guide, usage-based pricing is considered the most fair to customers since they only pay for what they’ve used. However, it comes with several challenges for the seller such as difficulties with revenue recognition.
The pricing model is mainly used by cloud companies such as Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services which allow clients to only pay for the resources they consumed over a particular period.
Pros
- The model feels fair to most customers
- Allows users to control spending by controlling their usage
- Price adapts to fluctuations in client use
Cons
- Difficulties with revenue recognition
- Billing is made in arrears rather than in advance
4. Per-User Pricing
The per-user pricing model charges clients based on the number of people using the product. So, if a software costs $10 and 5 people are using it, the client will pay $50.
The per-user or per-seat model is popular within the B2B SaaS industry and can be used to scale revenue targets since every seat is paid for.
A great example of a B2B SaaS brand using this model is Slack.

Pros
- Simple pricing model for customers to understand
- All paid users get full access to the product
- Generates lots of revenue for B2B SaaS
Cons
- Sharing of login credentials can be a challenge
- Requires significant infrastructure for provisioning
Conclusion
How you package your B2B SaaS product determines its uptake and eventual profitability. While subscription billing is the best way to offer your product to customers, you need to choose a subscription model that clearly demonstrates the value of your product and appeals to your customers.
Study the models discussed above and consider the pros and cons to identify the best subscription pricing model for your business.